Microglial Cells: Key Discoveries in Alzheimer’s Research
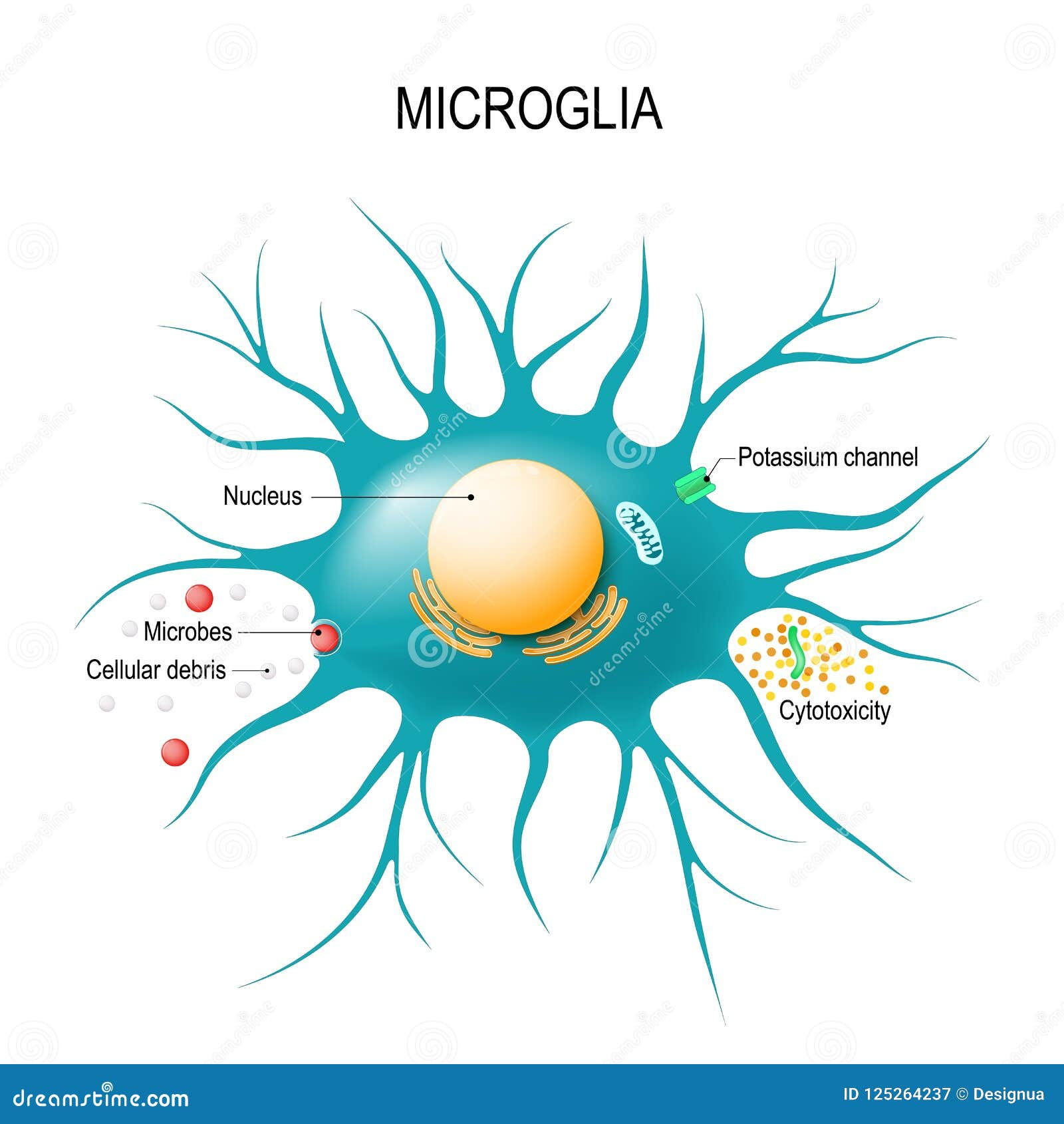
Microglial cells play a critical role as the brain’s immune defenders, constantly on the lookout for signs of damage or disease. These specialized cells are essential in maintaining brain health, as they are responsible for clearing out dead neurons and facilitating synaptic pruning — a process integral to the proper functioning of neural networks. Recent microglia research has revealed that abnormal functioning of these cells can contribute to various neurodegenerative diseases, most notably Alzheimer’s disease. By understanding the mechanisms behind microglial activity, scientists are hopeful for breakthroughs that could lead to new treatments and biomarkers for these debilitating ailments. As the estimated number of Americans living with Alzheimer’s continues to rise, the insights gained from studying microglial cells are more important than ever in combating the future of neurodegenerative diseases.
Also known as the brain’s resident immune cells, the roles of glial cells extend far beyond mere support functions. These cells are pivotal in monitoring the brain’s environment, responding to injury, and modulating inflammation, which can significantly influence neural health. The intricate process of synaptic remodeling governed by microglia is essential for cognitive development, yet disruptions in their function may pave the way for conditions such as Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative disorders. Investigations into microglial behavior are advancing our understanding of how the brain responds to pathological changes and injury. Thus, studying these brain immune cells is vital to unlocking new avenues for therapeutic interventions aimed at improving outcomes for patients suffering from these conditions.
Understanding the Role of Microglial Cells in Alzheimer’s Disease
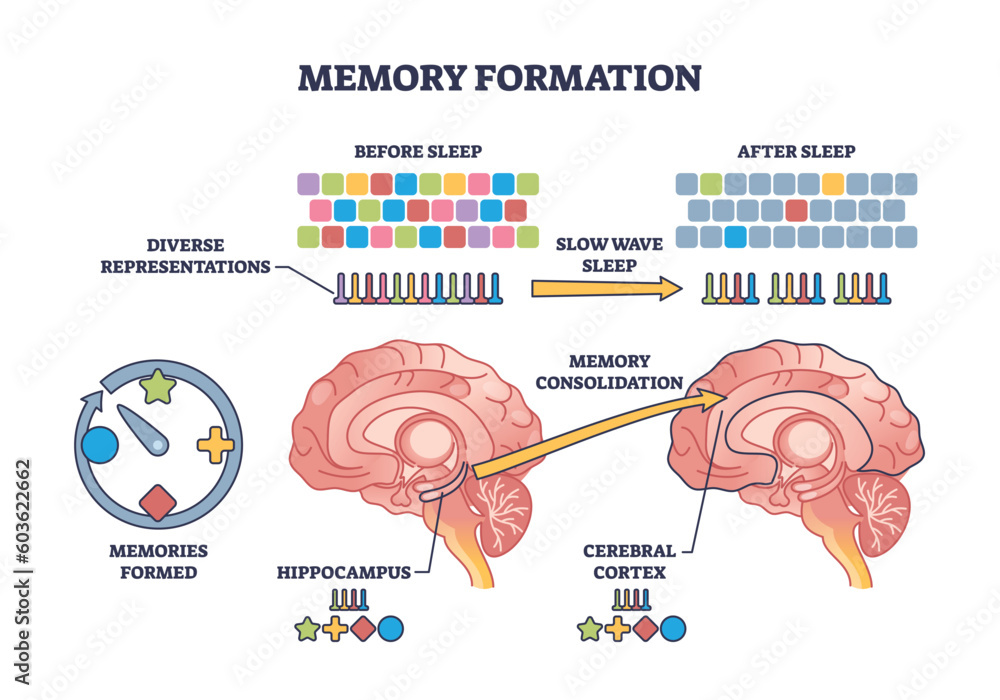
Microglial cells, often referred to as the brain’s immune guardians, play a pivotal role in managing the brain’s health, especially in the context of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. These specialized cells are responsible for monitoring the brain’s environment, detecting inflammation, and clearing away dead neurons through a process known as synaptic pruning. While this function is essential for maintaining cognitive function, it can also contribute to the progression of Alzheimer’s disease when microglial activation becomes dysregulated. Research has shown that overactive microglia can lead to excessive synaptic pruning, resulting in the loss of crucial neural connections that are necessary for memory and learning.
Current studies, particularly those conducted by Beth Stevens at Harvard, have provided groundbreaking insights into how microglial dysfunction relates to the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. By understanding how these cells respond to various stimuli in the brain, researchers are working to identify potential therapeutic targets that could mitigate the harmful effects of neuroinflammation. This rich field of microglia research is not just about recognizing the role of these cells in disease; it’s also about unraveling the complexities of the brain’s immune system and how it interacts with neuronal health to thwart the progress of neurodegenerative diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role do microglial cells play in Alzheimer’s disease?
Microglial cells serve as the brain’s immune system, playing a crucial role in Alzheimer’s disease by monitoring brain health, clearing dead cells, and participating in synaptic pruning. However, their abnormal activity can contribute to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s by disrupting normal synaptic function.
How do microglia contribute to synaptic pruning in neurodegenerative diseases?
Microglia are responsible for synaptic pruning, a process essential for healthy brain development and function. In neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s, overactive microglial cells can excessively prune synapses, leading to cognitive decline and disrupted neural communication.
Why is microglia research important for understanding neurodegenerative diseases?
Microglia research is vital as it uncovers the immune responses of the brain and how these cells influence the progression of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. Insights gained can lead to new therapeutic strategies and biomarkers that improve treatment outcomes for affected individuals.
What are the implications of abnormal microglial function in Alzheimer’s disease?
Abnormal microglial function can exacerbate neuronal damage and contribute to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Dysregulated synaptic pruning and inflammatory responses from microglia may lead to the loss of synapses and neurons, thereby worsening cognitive symptoms.
How can understanding microglial cells help in developing treatments for Alzheimer’s?
Understanding microglial cells can aid in the development of targeted treatments for Alzheimer’s by identifying how these immune cells behave in disease states. This knowledge can facilitate the creation of therapies that modulate microglial activity, ultimately protecting neurons and improving cognitive function.
What discoveries have been made about microglial cells in recent Alzheimer’s research?
Recent research highlighted the dual role of microglial cells in both protecting and harming the brain. Studies have shown how they can clear Alzheimer’s-associated plaques while also engaging in excessive synaptic pruning, thus unveiling potential targets for therapeutic intervention.
What is the relationship between microglial cells and neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease?
Microglial cells can initiate neuroinflammation in response to damaged neurons and amyloid plaques seen in Alzheimer’s disease. While this inflammation is meant to protect the brain, chronic activation of microglia can lead to neuroinflammatory processes that exacerbate neuron loss and dementia symptoms.
What impact does microglial research have on understanding the brain’s immune system?
Microglial research enhances our understanding of the brain’s immune system by revealing how these cells interact with neurons and respond to injury or disease. Insights from this research are crucial for developing new diagnostic tools and therapeutic strategies for neurodegenerative conditions.
How does the study of microglial cells influence the future of Alzheimer’s disease treatments?
Studying microglial cells influences the future of Alzheimer’s treatments by providing insights into the immune mechanisms of the brain. This knowledge can inspire innovative drug development aimed at modulating microglial activity to restore balance and protect cognitive function in affected patients.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Role of Microglial Cells | Microglial cells function as the brain’s immune system, identifying and responding to signs of illness and injury. |
| Pruning and Neurodegeneration | These cells help prune synapses during development but may also contribute to conditions like Alzheimer’s and Huntington’s diseases when abnormal pruning occurs. |
| Research Initiatives | Led by Beth Stevens, research at Boston Children’s Hospital focuses on understanding the role of microglial cells in neurodegenerative diseases. |
| Impact on Treatment | Discoveries in microglial research may lead to new biomarkers and treatments that could benefit the 7 million Americans with Alzheimer’s disease. |
| Importance of Fundamental Research | Stevens emphasizes the necessity of basic science in paving the way for advancements in understanding and treating diseases. |
Summary
Microglial cells play a crucial role in maintaining brain health by serving as the immune system of the brain. This research led by Beth Stevens has transformed our understanding of microglial functions, particularly their involvement in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. As these cells regulate synaptic pruning, improper functioning can lead to detrimental effects on neural circuitry, highlighting the importance of their study in developing new treatments. Through curiosity-driven research, significant strides are being made that promise hope for millions affected by neurodegenerative conditions.